
(A) A fatty acid chain (myristic acid) is (more.) The covalent attachment of either type of lipid can help localize a water-soluble protein to a membrane after its synthesis in the cytosol. Membrane protein attachment by a fatty acid chain or a prenyl group. Thus, the surface that the cell presents to the exterior is rich in carbohydrate, which forms a cell coat, as we discuss later. Like membrane lipids, membrane proteins often have oligosaccharide chains attached to them that face the cell exterior. A typical plasma membrane is somewhere in between, with protein accounting for about 50% of its mass.īecause lipid molecules are small compared with protein molecules, there are always many more lipid molecules than protein molecules in membranes-about 50 lipid molecules for each protein molecule in a membrane that is 50% protein by mass. By contrast, in the membranes involved in ATP production (such as the internal membranes of mitochondria and chloroplasts), approximately 75% is protein. In the myelin membrane, which serves mainly as electrical insulation for nerve cell axons, less than 25% of the membrane mass is protein.

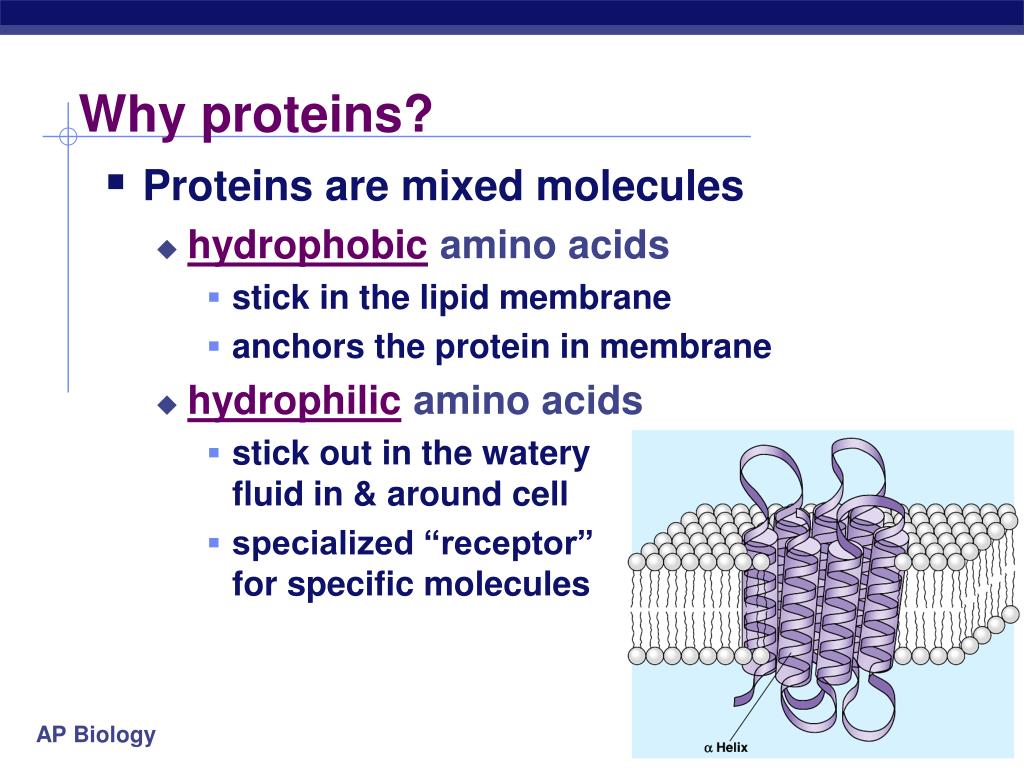
Accordingly, the amounts and types of proteins in a membrane are highly variable. It is the proteins, therefore, that give each type of membrane in the cell its characteristic functional properties. Hydrophobicity scales can also be obtained by calculating the solvent accessible surface areas for amino acid residues in the expended polypeptide chain or in alpha-helix and multiplying the surface areas by the empirical solvation parameters for the corresponding types of atoms.Although the basic structure of biological membranes is provided by the lipid bilayer, membrane proteins perform most of the specific functions of membranes. How do you know if amino acid is hydrophobic? Tyrosine is the only one of the aromatic amino acids with an ionizable side chain. Tyrosine and tryptophan absorb more than do phenylalanine tryptophan is responsible for most of the absorbance of ultraviolet light (ca. You can tell if a protein is hydrophobic or hydrophilic by examining the side chains of amino acids in its sequence. How do you know if a protein is hydrophobic or hydrophilic? 5-6), are relatively nonpolar (hydrophobic). Aromatic R Groups Phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan, with their aromatic side chains (Fig.

The secondary amino (imino) group is held in a rigid conformation that reduces the structural flexibility of the protein at that point. It helps in the function of organs responsible for making and regulating hormones, including the adrenal, thyroid, and pituitary glands.
HYDROPHOBIC AMINO ACIDS CELL MEMBRANE SKIN
Tyrosine also helps produce melanin, the pigment responsible for hair and skin color. Neurotransmitters help nerve cells communicate and influence mood. For example, even phenylalanine only has an aromatic ring, tyrosine is more soluble than it in water. The hydroxyl group attached to the aromatic gives it a polar characteristic while its aromatic ring gives it the hydrophobic characteristic. You might be interested: Question: How can i tell if a cat is pregnant? Why is phenylalanine more hydrophobic than tyrosine? 2.0 mg/ml at pH 9.5, the solubility is 1.4 mg/ml and at pH 10, the solubility is 3.8 mg/ml. The solubility in water (25 ☌) is 0.45 mg/ml in the pH range 3.2 – 7.5. This product is soluble in 1 M HCl (100 mg/ml), with heating. IMGT classes of the amino acids side chain properties Is phenylalanine hydrophilic or hydrophobic? The hydroxyl groups in these three amino acids are subject to an important type of posttranslational modification: phosphorylation (see below Nonstandard amino acids). Group II: Polar, uncharged amino acids Tyrosine possesses a hydroxyl group in the aromatic ring, making it a phenol derivative. There are only five atoms that will appear in your amino acid variable groups: H, C, N, O, and S. The lack of polarity means they have no way to interact with highly polar water molecules, making them water fearing. Hydrophobic amino acids have little or no polarity in their side chains.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
